
Charles Cameron is the regular guest-blogger at Zenpundit, and has also posted at Small Wars Journal, All Things Counterterrorism, for the Chicago Boyz Afghanistan 2050 roundtable and elsewhere. Charles read Theology at Christ Church, Oxford, under AE Harvey, and was at one time a Principal Researcher with Boston University’s Center for Millennial Studies and the Senior Analyst with the Arlington Institute:
A Hipbone Approach to Analysis III.
by Charles Cameron
I’ve been slowly prepping this series of pieces about my analytic approach — and the mysterious business of “connecting the dots” — for a while, but.. Jeff Jonas, whose work I only recently ran across, has given me “another piece of the puzzle” and a slew of new dots to connect, so here’s a quick impression of some new (for me) terrain that connects with other areas I have long been familiar with.
1
What it comes down to in my post today is this: I would like to reconcile “connecting the dots” with “putting together the pieces of the puzzle”.
Both metaphors have to do with “seeing the big picture”, and one of them (“connecting the dots”) has to do directly with nodes and edges, i.e. with those systems we call graphs and networks, while the other suggests a far subtler set of connections.
Consider this: n+1 is the next dot in the series of integers after n, with “+1” being the only link necessary — you can represent that on a 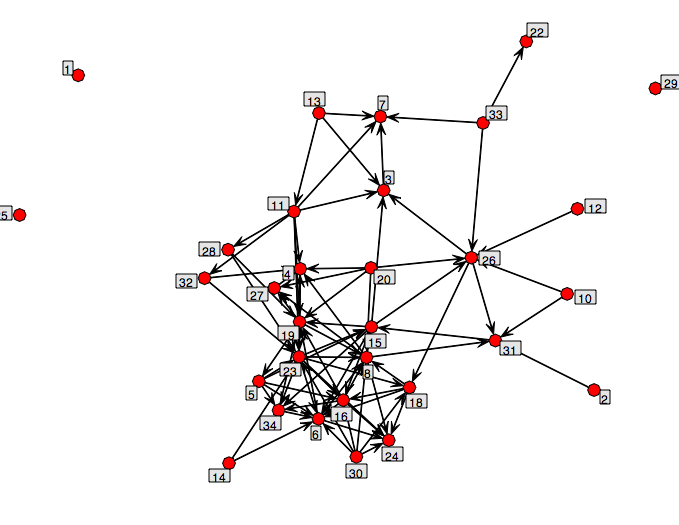 graph with two nodes and an edge. But if you had the sky of the northern hemisphere in one hand (hey, this is a thought experiment) and five square miles of landscape around Winchester Cathedral in the other, finding just where to fit the cathedral (and the surrounding, branching, leafy trees nearby) snugly into the sky would be a far trickier business, and the links between air and leaf and stone molecules would be very many — we should be grateful for the ease with which the sky accommodates itself in reality to the cathedral and the trees (and the cathedral and the trees to the sky) — and for the ease with which a painter like Turner can capture the effect…
graph with two nodes and an edge. But if you had the sky of the northern hemisphere in one hand (hey, this is a thought experiment) and five square miles of landscape around Winchester Cathedral in the other, finding just where to fit the cathedral (and the surrounding, branching, leafy trees nearby) snugly into the sky would be a far trickier business, and the links between air and leaf and stone molecules would be very many — we should be grateful for the ease with which the sky accommodates itself in reality to the cathedral and the trees (and the cathedral and the trees to the sky) — and for the ease with which a painter like Turner can capture the effect…
Two puzzle pieces, I mean, may have to fit along many aspects of their intersection, while dots can be connected by a single common thread.
2
I’ve only recently “met” the mind of Jeff Jonas, but he has some remarkable things to say about puzzles — for one thing, he writes about the levels of, well, computation involved in solving a jigsaw puzzle:
The first piece you take out of the box and place on the work surface requires very little computational effort. The second and third pieces require almost equally insignificant mental effort. Then as the number of pieces on the table grows the effort to determine where the next piece goes increases as well. But there is a tipping point where the effort to determine where to place the next piece gets easier and easier … despite the fact the number of puzzle pieces on the table continues to grow.
That in itself is a fascinating thought to dwell on, in fact it’s the sort of piece of the puzzle that gives me an epiphany — Jonas talks about puzzle pieces that provoke epiphanies, too:
Some pieces produce remarkable epiphanies. You grab the next piece, which appears to be just some chunk of grass – obviously no big deal. But wait … you discover this innocuous piece connects the windmill scene to the alligator scene! This innocent little new piece turned out to be the glue.
I’m processing this as a theologian / philosopher / poet, and Jonas has just given me a new angle on the theme of the intersection of frames of reference that Arthur Koestler in The Act of Creation takes to be the fundamental element in insights ranging all the way from casual jokes about rabbis to — let me give you a more powerful example — the Taniyama-Shimura Conjecture which, if I’ve understood the layman’s version correctly, began as a hunch that the otherwise entirely distinct mathematical zones known as “elliptic curves” and “modular forms” could be mapped onto each other – and wound up once proven, successfully bridging algebra with analysis.
Now, I am no no no no mathematician — but I am a student of conceptual bridges, so if I’ve phrased myself poorly here, please bear with me. The point is to think freshly about how one idea connects with another.
Koestler’s insight at the intersection between two fields (for this is essentially a matter of multiple-frame, and thus cross-disciplinary, thinking) is, I’d suggest, Jonas’ epiphanic piece of the puzzle.
Awesome.
3
But as we are trying to figure out the puzzle pieces — and this applies to “what is the meaning of life?” as much as to “what threat should be uppermost in our concern?” — Jonas has more to throw at us:
There may be more than one puzzle in the box, some puzzles having nothing to do with others. There may be duplicate pieces, pieces that disagree with each other, and missing pieces. Some pieces may have been shredded and are now unusable. Other pieces are mislabeled and/or are exceptionally well crafted lies.
I would like to add that puzzles may not be the only thing in the (universal) box. There’s a quote that originates somewhere in Heidegger, to the effect that “A puzzle is the unknown, to be solved, while a mystery is the unknowable, to be entered into and dwelt within.” As I say, I’ve only just run into Jonas’ thoughts, but I’d like to integrate that piece of the puzzle in with the ideas he’s providing – why not have a go at the mystery too while we’re about it?
4
So what happens with ideas? How do they connect?
Hermann Hesse, the Nobel laureate in literature who gave us Siddhartha and Steppenwolf and The Journey to the East, won his Nobel for his most ambitious novel, The Glass Bead Game (Das Glasperlenspiel, also known in English as Magister Ludi). It is an amazing piece of work that inspired at least one other book by another Nobel laureate — Manfred Eigen’s Laws of the Game: How the Principles of Nature Govern Chance — gave John Holland (he of genetic algorithms) the ruling metaphor for his life’s work, was an early and profound influence on Christopher Alexander’s thinking about pattern languages, and in general serves as a catalyst for grand scale creativity among a disparate crowd of very bright minds.
It is about a game — a game on the order of the complete works of JS Bach. And the essence of the game is the juxtaposition of thoughts.
It is about “connecting the dots” and “putting together the pieces of the puzzle” on the grand scale, to create not a single link between ideas, not a small “bigger picture” deploying a half-dozen or so insights, but a vast architecture of ideas that encompasses all “deep” human thought and connects all “beautiful” cognizable patterns. Hesse uses the image of an organist playing an organ to describe the play of ideas that composes his Game, writing:
All the insights, noble thoughts, and works of art that the human race has produced in its creative eras, all that subsequent periods of scholarly study have reduced to concepts and converted into intellectual values the Glass Bead Game player plays like the organist on an organ. And this organ has attained an almost unimaginable perfection; its manuals and pedals range over the entire intellectual cosmos; its stops are almost beyond number.
And in Hesse’s central, musical metaphor, the myriad thoughts that comprise what he terms the “hundred-gated cathedral of Mind” are linked one with another by likeness — by identity, isomorphism, homology, symmetry, parallelism, opposition, analogy, metaphor…
5
I’ll have to move us deep into the territory of the arts and humanities here, because Hesse himself was supremely versed in those areas, but in doing so I would remind you that John Holland wrote of his life’s work, “If I could get at all close to producing something like the glass bead game I can’t think of anything that would delight me more.”
Here’s Hesse on the analogical / isomorphic nature of the moves that connect ideas — “only connect!” said EM Forster — in his great Game:
Throughout its history the Game was closely allied with music, and usually proceeded according to musical or mathematical rules. One theme, two themes, or three themes were stated, elaborated, varied, and underwent a development quite similar to that of the theme in a Bach fugue or a concerto movement. A Game, for example, might start from a given astronomical configuration, or from the actual theme of a Bach fugue, or from a sentence out of Leibniz or the Upanishads, and from this theme, depending on the intentions and talents of the player, it could either further explore and elaborate the initial motif or else enrich its expressiveness by allusions to kindred concepts. Beginners learned how to establish parallels, by means of the Game’s symbols, between a piece of classical music and the formula for some law of nature. Experts and Masters of the Game freely wove the initial theme into unlimited combinations. For a long time one school of players favored the technique of stating side by side, developing in counterpoint, and finally harmoniously combining two hostile themes or ideas, such as law and freedom, individual and community. In such a Game the goal was to develop both themes or theses with complete equality and impartiality, to evolve out of thesis and antithesis the purest possible synthesis.
It is Bach, it is Hegel, it is the very essence of creativity, it is the associative, metaphoric nature of mind and brain (and I won’t get more than toe-deep in the “deep problem” of consciousness here).
6
And it does involve combining the understanding of both puzzle and mystery, to return to that distinction from Heidegger:
I suddenly realized that in the language, or at any rate in the spirit of the Glass Bead Game, everything actually was all-meaningful, that every symbol and combination of symbols led not hither and yon, not to single examples, experiments, and proofs, but into the center, the mystery and innermost heart of the world, into primal knowledge. Every transition from major to minor in a sonata, every transformation of a myth or a religious cult, every classical or artistic formulation was, I realized in that flashing moment, if seen with a truly meditative mind, nothing but a direct route into the interior of the cosmic mystery, where in the alternation between inhaling and exhaling, between heaven and earth, between Yin and Yang, holiness is forever being created.
Hesse is proposing his intuition that the world of ideas is a mandala-form array of symmetries with a “vanishing point” in the center.
Well, I have leapt far from my original topic, Jeff Jonas’ comments on piecing together a puzzle, but I hope the bungee-cord I’ve been depending on has held your attention, and now as always, at the far end of the extension there’s a bouncing-back.
7
The human mind “connects the dots” and “pieces together the puzzle” by recognizing likenesses — pattern recognition, if you like.
But just how human analogical thinking functions is not exactly an easy question…

 graph with two nodes and an edge. But if you had the sky of the northern hemisphere in one hand (hey, this is a thought experiment) and five square miles of landscape around Winchester Cathedral in the other, finding just where to fit the cathedral (and the surrounding, branching, leafy trees nearby) snugly into the sky would be a far trickier business, and the links between air and leaf and stone molecules would be very many — we should be grateful for the ease with which the sky accommodates itself in reality to the cathedral and the trees (and the cathedral and the trees to the sky) — and for the ease with which a painter like Turner can capture the effect…
graph with two nodes and an edge. But if you had the sky of the northern hemisphere in one hand (hey, this is a thought experiment) and five square miles of landscape around Winchester Cathedral in the other, finding just where to fit the cathedral (and the surrounding, branching, leafy trees nearby) snugly into the sky would be a far trickier business, and the links between air and leaf and stone molecules would be very many — we should be grateful for the ease with which the sky accommodates itself in reality to the cathedral and the trees (and the cathedral and the trees to the sky) — and for the ease with which a painter like Turner can capture the effect…
 officials out of those regions (the book to read is
officials out of those regions (the book to read is 

